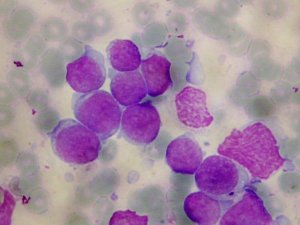
Researchers found that the presence of a few remaining leukemia cells, called minimal residual disease (MRD), at the end of induction chemotherapy was not predictive of risk or outcome in children with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). This opens the possibility for patients with T-cell ALL who have MRD to achieve complete remission without undergoing intensified cancer treatments and their associated toxicities.
Category: children
Educating the immune system to prevent allergies
With the arrival of spring, millions of people have begun their annual ritual of sneezing and wheezing due to seasonal allergies. A research team is bringing them hope with a potential vaccine that nudges the immune response away from developing allergies. The findings have major clinical implications since allergies and asthma often start in childhood and for which there is presently no cure.
Children’s views should shape how research is conducted, says ethics body
A new report calls for a change in culture across all areas of children’s health research, so that children’s and young people’s views and opinions can help to shape how research is prioritized, designed and reviewed. Unless ethical concerns about asking children to take part in research are addressed, our understanding of childhood disorders and ability to provide evidence based care will remain limited.
Bullying: What we know based on 40 years of research
Psychologists have reviewed over 40 years of research on bullying among school age youth, documented the current understanding of the complexity of the issue and suggested directions for future research.
Study matches infant stiff-joint syndromes to possible genetic origins
For the first time, a study has matched dozens of infantile diseases and syndromes involving muscle weakness and stiff joints to their likely genetic origins. The study’s goal is to better enable physicians and geneticists to advance new treatments that might help these children.
Can drinking alcohol harm the child before the mother knows she is pregnant?
Alcohol drunk by a mouse in early pregnancy changes the way genes function in the brains of the offspring. The early exposure was also later apparent in the brain structure of the adult offspring. The timing of the exposure corresponds to the human gestational weeks 3-6 in terms of fetal development.
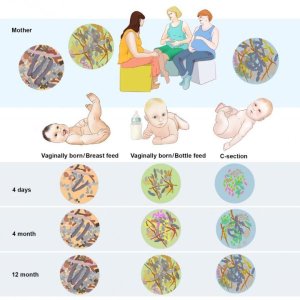
The infant gut microbiome: New studies on its origins and how it’s knocked out of balance
A fecal sample analysis of 98 Swedish infants over the first year of life found a connection between the development of a child’s gut microbiome and the way he or she is delivered. Babies born via C-section had gut bacteria that showed significantly less resemblance to their mothers compared to those that were delivered vaginally.
Depression intensifies anger in veterans with PTSD
The tendency for veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder to lash out in anger can be significantly amplified if they are also depressed, according to new research.
What to do – and what not to – if a friend’s child is going to die
Children’s Hospice Week: When your child is given a terminal diagnosis, friendships become more important than ever. Bereavement counsellor Heather Tilley explains what to do – and what not to – if a friend gets the worst possible news
Are some children born naughty?
A new Channel 4 series about children with serious behavioural issues asks if nature can take the blame – rather than the long-suffering parents
Infectious-Disease Expert Debunks Common Vaccine Myths
Decades of studies show they are very safe, and highly effective in saving kids from illness and death Source: HealthDay