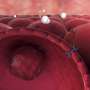
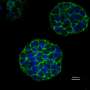
A key mechanism in the regulation of blood sugar levels has been identified in work led by A*STAR researchers. The findings could help us understand the mechanisms of diabetes and might lead to new treatments.
Category: Research
3D printer generates realistic model of a cancerous tumour
An international scientific team has successfully created a three-dimensional model of a cancerous tumour using a 3D printer. Their model could ultimately help discover new drugs and cast new light on how tumours develop, grow and spread.
Life-prolonging protein could inhibit ageing diseases
Researchers have found a molecule that plays a key link between dietary restriction and longevity in mammals. This discovery may lead to the development of new therapies to inhibit age-related diseases.
Clinical trial reduces stress of cancer caregivers
Stem cell transplant is essential in the care of many blood cancers, but leaves patients requiring in-home care for months after.
Doctors’ checklist could help decrease length of COPD patients’ hospital stay
Patients with worsening chronic obstructive pulmonary disease spend less time in hospital when their doctors manage their care by using a checklist of steps called order sets.
Baby brain study identifies health problems in premature infants
Queensland scientists are part of an international team that has developed a tool to identify health problems in premature babies.
Koch tells Health Minister to ‘get a backbone’, resigns from organ donation advisory council
Television presenter David Koch resigns as chairman of the Organ and Tissue Authority Advisory Council in protest over the Government’s handling of a review into organ donation.
Scientists discover Ebola virus’s Achilles heel
US researchers believe they may have pinpointed the Achilles heel of the Ebola virus, which could hold the key to developing an effective preventative vaccine, a new study reveals.
Higher-Tech Fake Eggs Offer Better Clues To Wild-Bird Behavior
Faux eggs made with 3-D printers are better than sculpted versions, researchers say, because it’s easier to systematically vary their size, weight and other features. Next goal: 3-D fragile shells.» E-Mail This
New urine test could reduce need for blood samples
If you’ve been to the doctor, you probably know what to do when you’re handed a plastic cup and shown to the bathroom.
Study identifies Ebola virus’s Achilles’ heel
An international team including scientists from Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University and the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID) has identified the molecular “lock” that the deadly Ebola virus must pick to gain entry to cells. The findings, made in mice, suggest that drugs blocking entry to this lock could protect against Ebola infection. The study was published in today’s edition of the online journal mBio.