An interdisciplinary research team led by the deans of Virginia Commonwealth University’s Schools of Medicine and Engineering has for the first time explained the association between human height and a specific protein-coding gene that is found in sperm.
Category: Research
Modifying stem cells shows initial promise in battle against muscular dystrophy
A group of University of Florida Health researchers has found a way to reverse the effects of one type of muscular dystrophy by editing the genome of nervous system stem cells.
Hacking the nervous system
When Maria Vrind, a former gymnast from Volendam in the Netherlands, found that the only way she could put her socks on in the morning was to lie on her back with her feet in the air, she had to accept that things had reached a crisis point. “I had become so stiff I couldn’t stand up,” she says. “It was a great shock because I’m such an active person.”
Hearing voices in your head more common than thought: study
Hearing voices in your head is more common than most people might think, new research by the University of Queensland finds.
Five perspectives on HIV prevention pill awaiting Australian approval
Australia’s ambitious goal of no new cases of HIV by 2020 will be a tough deadline to meet given rates have been steadily increasing since 2000. Here, the ABC hears five perspectives on a major breakthrough in the fight against the epidemic — the preventative drug known as PrEP.
Scientists Discover Evidence Of A 435,000-Year-Old Murder
Scientists say it’s not just a murder from another era, but also part of one of the earliest mass graves.» E-Mail This
Australian researchers find new hope for ovarian cancer treatment
Australian researchers say they now know why ovarian cancer becomes resistant to chemotherapy and some drugs.
Signal identified that prompts one kidney to grow larger when the other is lost
Scientists have found an explanation for the century-old observation that if you end up with just one kidney, the lone organ gets bigger.
Precision medicine is ‘personalized, problematic, and promising’
The rapidly emerging field of precision medicine is a “disruptive innovation” that offers the possibility of remarkably fine-tuned remedies to improve patient health while minimizing the risk of harmful side effects, says J. Larry Jameson, MD, PhD, dean of the Perelman School of Medicine and executive vice president of the University of Pennsylvania for the Health System, in this week’s issue of the New England Journal of Medicine. Writing with oncologist Dan L. Longo, MD, a professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, in a “Sounding Board” piece, Jameson surveys the terrain of the new field.
How A Claim That A Childhood Vaccine Prevents Leukemia Went Too Far
It seemed to make sense that the childhood Hib vaccine could cut leukemia risk by keeping the immune system in check. But proving there’s cause and effect at work turns out to be a challenge.» E-Mail This
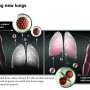
Researchers taking bold steps toward engineering new lungs
According to the World Health Organization, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) currently affects more than 64 million people worldwide and is poised to become the third leading cause of mortality by 2030.